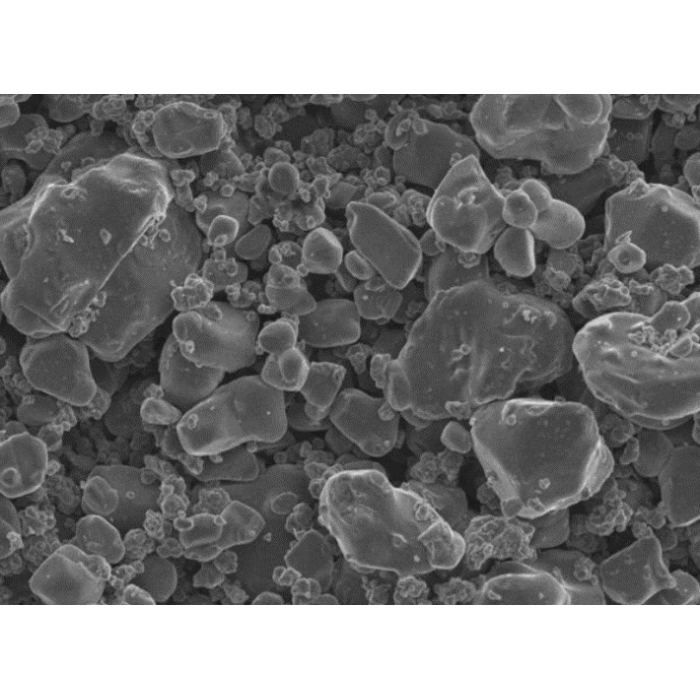
High Voltage, High Capacity Lithium Cobalt Oxide, LiCoO2 (LCO) Powder, 500g, 14.0~ 18.0 um D50, Cathode Material
John B. Goodenough's research group first discovered lithium cobalt oxide as an intercalation electrode in 1980. Lithium cobalt oxide is now widely used as the cathode material of choice in rechargeable lithium-ion batteries found in consumer electronics products. Although the theoretical capacity of traditional LiCoO2 is 273.8 mAh/g, its capacity is limited by the voltage range (3.0~4.2 V) due to the irreversible phase transition LiCoO2 of above 4.2 V. This novel LiCoO2 can be cycled up to 4.5 V (4.4 V recommended) with high capacity. It can typically deliver a capacity of 190.6 mAh/g at 0.1 C and 180.2 mAh/g at 1 C when cycled between 3.0 and 4.5 V.
Product No.: PO5001
Package Size: 500g
Specifications:
CAS Number: 12190-79-3
Appearance: Black powder
Molecular Formula: LiCoO2
Purity: >99.5%
Formula Weight: 97.88 g/mol
Synonym: Lithium Cobaltite
Chemical Name or Material: Lithium Cobalt (III) Oxide
Particle sizes:
D10: ≥4.0 µm
D50: 14.0~18.0 µm
D90: ≤45.0 µm
TAP density: ≥2.4 g/cm3
BET Specific Surface Area: 0.10 ~ 0.30 m2/g
pH: ≤10.8
Discharge Capacity (mAh/g): ≥188 (typical 190.6) @0.1 C; ≥175 (typical 180.2) @1 C, (vs. Li, 0.1 C, 3.0~ 4.5 V, coin cell)
Efficiency: ≥95% @0.1 C (vs. Li, 0.1 C, 3.0~4.5 V, coin cell)
| Chemical Analysis | wt% |
| Li | 7.0±0.5 |
| Co | 59.0~61.0 |
| Na | ≤0.02 |
| Ca | ≤0.02 |
| K | ≤0.01 |
| Cr | ≤0.005 |
| Cd | ≤0.005 |
| Pb | ≤0.001 |
| Cu | ≤0.005 |
| Fe | ≤0.015 |
| Mn | ≤0.02 |
| Moisture | ≤0.10 |
| Residual Li2CO3 | ≤0.06 |
References: